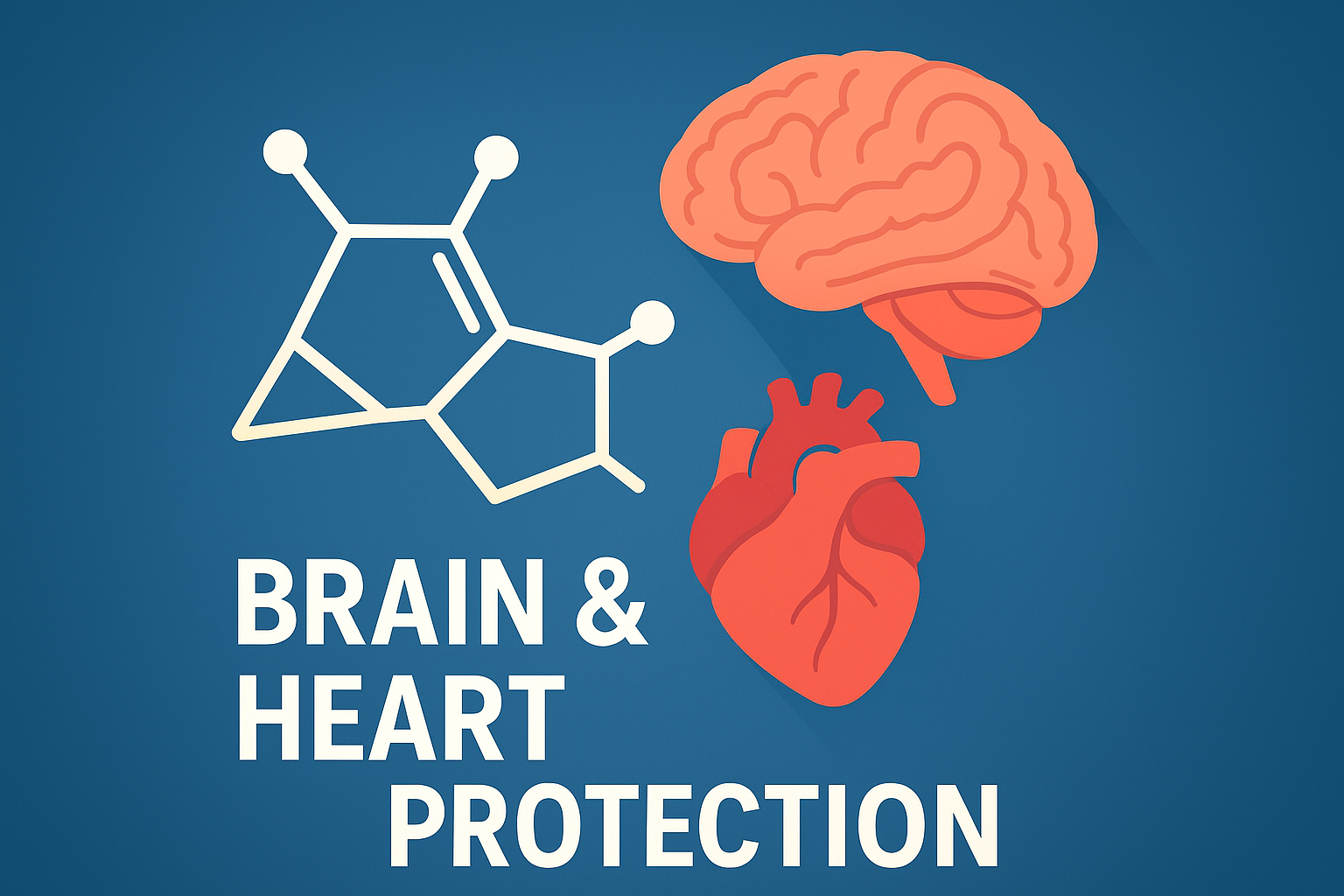
Chinese researchers have patented a new class of norbornene derivatives that show promise in treating cardiovascular and neurological disorders. The compounds were developed by scientists at Jiangsu Hengrui Pharmaceuticals Co. Ltd., Shanghai Senhui Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., and Shanghai Shengdi Medicine Co. Ltd.
Patent Covers Broad Therapeutic Use
The new patent claims chemical structures derived from norbornene, a bicyclic hydrocarbon known for its strong and flexible molecular framework. According to the filing, the compounds may be used to treat cerebral infarction, coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, and cerebral ischemia.
Researchers say the derivatives can help reduce brain and heart tissue damage caused by restricted blood flow, a key factor in stroke and heart attack.
Promising Preclinical Data
One example compound, identified as Compound 1 (Example 1) in the patent, showed encouraging results in animal tests. In a rat model of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO)—a standard method for studying stroke—the compound improved neurological function scores and significantly reduced cerebral infarct size.
These findings suggest that the norbornene-based molecules may protect brain tissue from ischemic injury and improve recovery after a stroke.
A Step Toward Novel Cardiovascular Therapies
Cardiovascular and ischemic brain disorders remain major global health challenges. Current treatments often focus on managing symptoms rather than repairing damage. The new patent could open the door to novel neuroprotective and cardioprotective drugs that act at the molecular level to limit cell death.
The involvement of Jiangsu Hengrui, one of China’s leading pharmaceutical innovators, highlights the country’s growing role in global drug discovery and intellectual property generation.
Early Stage, but Strong Potential
The norbornene derivatives are still at an early research stage. Human trials have not yet been announced. However, securing a patent gives the developers exclusive rights to further research, licensing, or partnership opportunities.
Experts note that norbornene’s unique ring structure allows scientists to design molecules with precise pharmacological activity and stability, making it a versatile scaffold in modern medicinal chemistry.
China’s Rising Innovation in Medicinal Chemistry
In recent years, Chinese pharmaceutical firms have filed a growing number of patents in cardiovascular, oncology, and neurological drug categories. This trend reflects China’s ambition to shift from generic drug manufacturing toward innovative, IP-driven R&D.
The latest norbornene patent strengthens that trajectory and adds another example of homegrown chemical innovation aimed at life-threatening diseases.