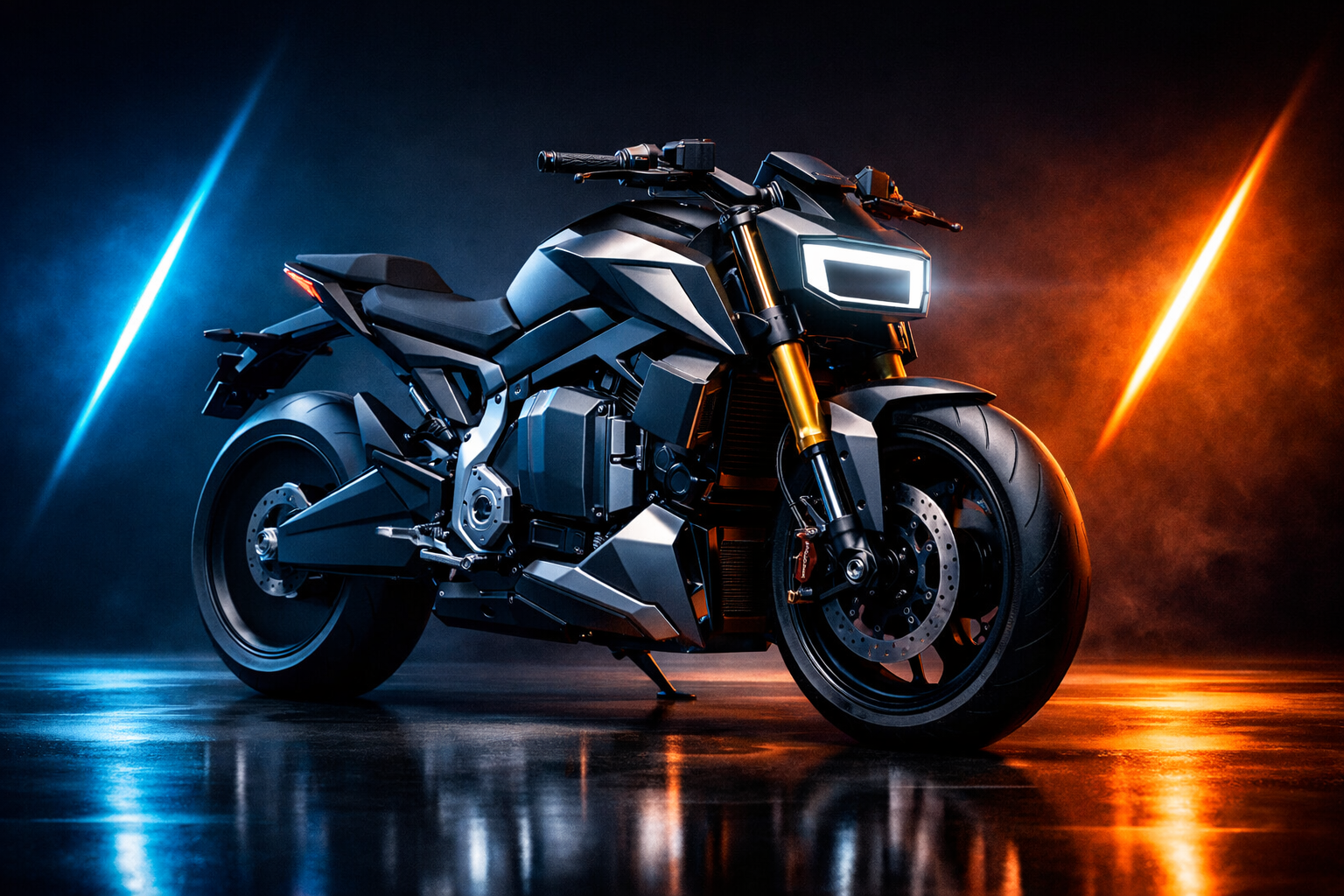
TVS Motor Company has taken a decisive step toward the future of electric motorcycling. The company has secured a design patent in India for its eFX 3O electric motorcycle concept, a machine that first stunned global audiences with its radical styling and aggressive stance. This patent filing sends a clear message. TVS is no longer testing the waters. It is preparing to compete seriously in the premium electric motorcycle space.
At a time when India’s electric two-wheeler market remains dominated by scooters, the eFX 3O patent signals a strategic shift. TVS appears ready to challenge conventions, push design boundaries, and redefine how electric motorcycles are perceived in the country.
A Concept That Refuses to Be Ignored
The TVS eFX 3O made its debut as a concept motorcycle at EICMA, the world’s biggest two-wheeler show. From the moment it rolled onto the stage, it stood apart. Unlike conservative electric bikes that mimic petrol models, the eFX 3O embraced a futuristic, uncompromising identity.
Now, with its design patented in India, the concept has moved closer to reality.
A design patent does not confirm production. But it strongly indicates intent. Manufacturers rarely invest in patent protection unless they see long-term value. In TVS’s case, the move suggests that the eFX 3O could evolve from a showpiece into a road-ready machine.
Sharp Design Sets the Tone
The patented design reveals a motorcycle that looks fast even when standing still. The eFX 3O uses angular body panels, a sharply sculpted fuel-tank-style battery housing, and a minimalist rear section. Every line looks deliberate. Every surface feels purposeful.
The front end grabs attention immediately. A rectangular LED headlamp replaces traditional round or oval units. It gives the bike a robotic, almost cyberpunk character. Slim LED indicators and clean surfaces reinforce the futuristic theme.
In contrast to bulky electric motorcycles that hide their components, the eFX 3O proudly displays its mechanical elements. The battery pack remains partially exposed. The motor and belt drive sit in plain view. This approach emphasizes performance and honesty in design.
Chassis and Hardware Speak Performance
The eFX 3O design patent also highlights premium underpinnings. The motorcycle features upside-down front forks, a setup typically reserved for performance-oriented bikes. At the rear, a monoshock suspension supports a compact and athletic stance.
The wheels appear solid or partially covered, reducing visual clutter and improving aerodynamics. Disc brakes at both ends suggest strong stopping power, while the design hints at the possibility of dual-channel ABS in a production version.
Compared to current electric motorcycles in India, which often rely on basic hardware to control costs, the eFX 3O looks unapologetically premium.
Riding Posture Focuses on Engagement
The patented images show a rider-centric layout. The seat sits low and flat. The handlebars appear slightly forward-set. The foot pegs suggest a sporty yet usable riding triangle.
This setup contrasts sharply with commuter-focused electric bikes that prioritize upright comfort over engagement. TVS seems to be targeting riders who value control, feedback, and excitement.
The eFX 3O does not try to please everyone. It aims to attract enthusiasts.
Technology Still Under Wraps
TVS has not disclosed technical specifications for the eFX 3O. The patent focuses only on design, not engineering details. However, the layout provides clues.
The motorcycle likely uses a mid-mounted electric motor paired with a belt drive. This configuration improves weight distribution and reduces unsprung mass. It also enhances ride quality and handling.
The visible battery housing suggests a fixed battery pack rather than a removable unit. This choice aligns with performance goals, as fixed batteries allow better structural rigidity and higher energy density.
Compared to electric scooters and entry-level electric bikes, which prioritize convenience, the eFX 3O appears designed for dynamic performance.
How It Compares to the Current EV Market
India’s electric two-wheeler market tells a clear story. Scooters dominate sales. Electric motorcycles remain niche. Most available options focus on affordability rather than aspiration.
TVS seems determined to change that narrative.
Unlike commuter-style electric bikes, the eFX 3O targets the premium lifestyle segment. It competes on design, presence, and brand image rather than price alone. This strategy mirrors global trends, where electric motorcycles increasingly emphasize identity and emotion.
When compared with petrol motorcycles in the same visual class, the eFX 3O does not feel like a compromise. It looks like a clean-sheet design, free from legacy constraints.
Strategic Importance for TVS
TVS already holds a strong position in India’s electric scooter market with the iQube. However, scooters alone cannot define an electric future. Motorcycles remain central to India’s two-wheeler culture.
By patenting the eFX 3O design, TVS signals its ambition to lead, not follow.
The move also strengthens TVS’s global image. A bold electric motorcycle aligns with international markets where premium EVs command attention and higher margins. It positions TVS as a technology-driven manufacturer capable of innovation beyond mass-market products.
Production Timeline Remains Unclear
Despite the excitement, TVS has not announced a launch timeline. The eFX 3O remains a concept on paper and in patent drawings.
Industry watchers expect that if TVS greenlights production, the motorcycle could arrive between 2026 and 2027. Pricing would likely place it in the premium segment, possibly above mainstream petrol motorcycles but competitive with global electric offerings.
Much will depend on battery costs, charging infrastructure, and consumer readiness.
A Clear Message to the Industry
The eFX 3O design patent delivers a powerful message. TVS believes electric motorcycles deserve bold design and serious intent. The company refuses to treat EVs as secondary products.
In comparison to cautious rivals, TVS appears confident. It is willing to experiment. It is willing to invest. And it is willing to lead.
Conclusion: More Than Just a Patent
The TVS eFX 3O is more than a patented design. It represents a mindset shift. It challenges the idea that electric motorcycles must be dull, slow, or purely practical.
If TVS brings this concept to life, it could redefine expectations in India’s electric two-wheeler market. The patent may be silent on specifications. But its message is loud and clear.
The electric motorcycle era is coming. TVS wants to shape it.